Improvement in healthcare delivery for India’s 104 million tribal people poses a major challenge to the country’s ability to meet the health and nutrition targets set by the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for 2030.
As evident from data in the tribal policy brief, compared to India’s overall population, tribal communities suffer from higher maternal and under-five mortality; stunted, wasted, and underweight children; higher incidence of malaria and tuberculosis; and a high and growing burden of diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and hypertension. Therefore, without an explicit and concerted focus on delivering quality healthcare services to its tribal populations, India runs the risk of excluding and further marginalising them, as well as undermining its efforts to reach SDG 2 on hunger, and SDG 3 on health and wellbeing.
Related article: India’s first comprehensive tribal health report
To dive deeper into these issues and explore possible solutions for scaled impact, a joint team of Piramal Swasthya and The Bridgespan Group recently undertook extensive research (including interviews and field visits) on the tribal health challenges confronting India. This builds on Piramal Swasthya’s work in the tribal mandals of Visakhapatnam district as well as in the 25 NITI Aayog-mentored Aspirational Districts.
Based on our study, we concluded that ending preventable deaths and reducing morbidity in tribal areas will require major investment in building strong and functioning primary healthcare systems with robust referral chains. Any such action also needs to overcome the significant barriers that tribal populations face in terms of access to, and awareness of quality healthcare.
1. Barriers in accessing healthcare services
Most tribal people live in hilly, forested areas that are difficult to reach. The majority are scattered across two regions: Central India (i.e., Southern Rajasthan, Eastern Gujarat, Northern Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Odisha) and Northeastern India (i.e., Meghalaya, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Tripura, Sikkim, Nagaland, and Mizoram).1
In many cases, remote areas lack motorable roads and transport facilities. For example, to reach Nanda, a habitation in the tribal mandals of Araku in Visakhapatnam, healthcare providers from Araku town commute 34 kilometres, of which they have to trek over hilly terrain for 14 kilometres, carrying their bags of equipment and health records.
Now imagine the same commute, in reverse, for a tribal woman in labour to reach the nearest health centre; and particularly if she needs a caesarean delivery, to reach the suitably equipped district hospital in time. In regions that are susceptible to violence and political turbulence, such travel becomes even more precarious.
2. Barriers in accessing information about health practices
Traditional and socio-cultural beliefs, norms, and practices, combined with a lack of understanding of these practices by modern medicine, make tribal communities reluctant to seek formal care. In addition, linguistic differences alienate tribal people and hinder their understanding of, and access to care.
It takes focused efforts to enable tribal people to see value in institutional delivery or preventive health practices for pregnant women and newborns.
As a result, even in emergency situations such as a snakebite, tribal communities typically prefer to first visit a local healer. This usually leads to a higher number of preventable deaths due to snakebite, as patients are often brought to modern healthcare facilities too late.
In a similar vein, it takes focused efforts, often over a long period, to enable tribal people—including community leaders—to see value in institutional delivery or preventive health practices for pregnant women and newborns.
Successful healthcare delivery models in tribal districts by nonprofits such as SEARCH, Ekjut, and Jan Swasthya Sahayog are grounded in first building rapport and trust with the tribal communities by spending time with them, as well as by enabling and empowering them to participate in the delivery of healthcare services. This has not only improved their health seeking behaviour, but has also resulted in positive health outcomes.
However, such community-led practices have not been replicated across all tribal regions in India, and there is an inadequate representation of the communities’ voice and agency in managing their own health.
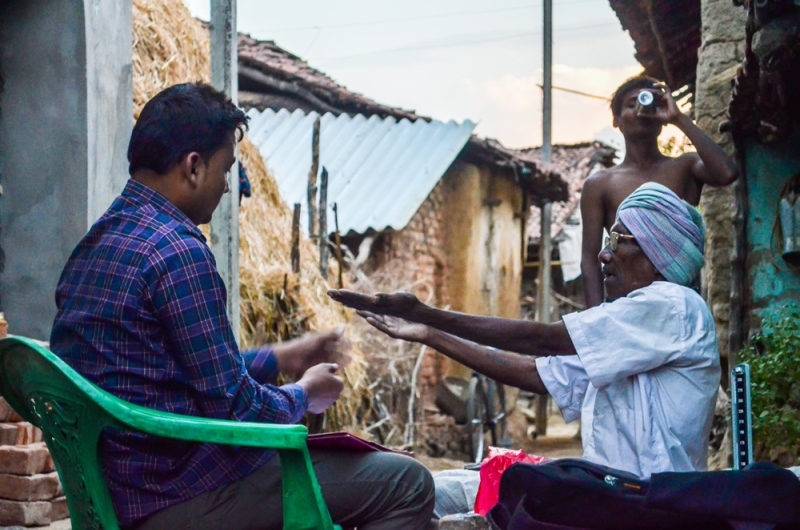

Traditional and socio-cultural beliefs, norms, and practices, combined with a lack of understanding of these practices by modern medicine, make tribal communities reluctant to seek formal care. | Picture courtesy: SEARCH
3. Shortfall of public health facilities
The above challenges are compounded by the severe shortfall in public health facilities and trained workforce in tribal areas. Per government guidelines, tribal and hilly areas should have one Health Sub Centre (HSC) per 3,000 population, one Primary Health Centre (PHC) per 20,000 population, and one Community Health Centre (CHC) per 80,000 population. In about half of the Indian states, the number of health institutions in tribal areas fall below the norm by 27–50 percent. For example, Madhya Pradesh reported a shortfall of 10 percent HSCs, 41 percent PHCs, and 38 percent CHCs in its tribal districts, while Jharkhand reported a shortfall of 37percent HSCs, 69 percent PHCs, and 29 percent CHCs in its tribal districts.2 Analysing the data from Rural Health Statistics 2018, there was an 82.3 percent shortage in specialists at Community Health Centres in tribal areas.
Further, there is poor understanding of what constitutes quality care, absence of systematic technical training of health workforce, and lack of systems and incentives to rigorously monitor and deliver quality services.
Related article: Why does undernutrition persist in India’s tribal populations?
4. Lack of data
Lastly, there is almost a complete lack of reliable tribal-specific health data, to inform policies and health interventions specific to the needs of the diverse tribal communities. These range from lack of data on the incidence and prevalence of disease in tribal areas to a lack of knowledge about what health solutions work locally and why.
Unfortunately, over the last few decades, few scaled solutions have emerged to address these dire health gaps. Several locally focused nonprofits and operating foundations are positively impacting the lives of tribal communities. For example, SEARCH has not only transformed the lives of the tribal people of 48 villages in Gadchiroli,3 but has also demonstrated the model of home-based neonatal care. Similarly, Jan Swasthya Sahayog in Bilaspur, Chhattisgarh; Ekjut India in Chakradharpur, Jharkhand; Tribal Health Initiative in Sittilingi, Tamil Nadu; SEWA Rural in Bharuch, Gujarat; Tata Steel CSR in Jharkhand and Odisha; and a few other organisations; work deeply on different aspects of tribal and rural healthcare services.
However, given the diversity, geographic spread, and unmet health needs of India’s tribal population, none of these models have yet been scaled or replicated to bring about sizeable impact. The work of these nonprofits is also constrained by inadequate funding, lack of a robust evidence base to inform policy, lack of knowledge sharing, and limited experience of working with government health systems.
The report by the expert committee on tribal health, chaired by Dr Abhay Bang, in 2018 recommended the creation of a functional, universal, and sustainable system of healthcare for tribal people by 2022. The government is yet to take action on the committee’s recommendations.
India urgently needs collaborative action to provide quality healthcare that is accessible to, and welcoming of tribal communities.
Given the magnitude of the challenge and the national aspiration to attain the SDG 2 and SDG 3 targets for nutrition and health respectively, India urgently needs collaborative action to provide quality healthcare that is accessible to, and welcoming of tribal communities. No single funder or stakeholder, however capable, can single-handedly solve this issue, particularly by the SDG 2030 timeline. To bring about population-level change, local communities, government, implementing organisations, research agencies, and funders must join forces to bring about systemic and scaled health impact.
Collaboration can facilitate on-ground implementation of interventions to improve both tribal healthcare demand and service delivery, as well as develop and disseminate knowledge of what works and what does not. This can be enabled by a user-friendly and interoperable technology platform for better governance and accountability.
Such collaborative action at a systemic level requires a deep and long-term commitment of human, financial, and social capital resources by all stakeholders involved. Whilst irreversible improvements in tribal health outcomes will likely not be quick or straightforward, India no longer has the luxury of continuing to wait and watch as millions of its tribal peoples suffer and die from preventable causes.
- Expert Committee on Tribal Health. Tribal Health in India: Bridging Gaps and a Roadmap for Future. New Delhi (India): MoFHW, India; 2018. (pg. 12-13)
- Rural Health Statistics 2018
- Annual Report 2017-18, SEARCH Society for Education, Action and Research in Community Health, pg 8.
—
Know more
- Read the Tribal Health Policy Brief, a report by the Government of India’s expert committee on tribal health.
- Read this paper by the National Institute of Research in Tribal Health (NIRTH) on the challenges of tribal health in Odisha.
- Track the performance of the Aspirational Districts on health, nutrition, and other indicators.
Do more
- Connect with the authors Dr Shailendra Hegde and Pritha Venkatachalam to join the collaborative action to improve tribal health outcomes.