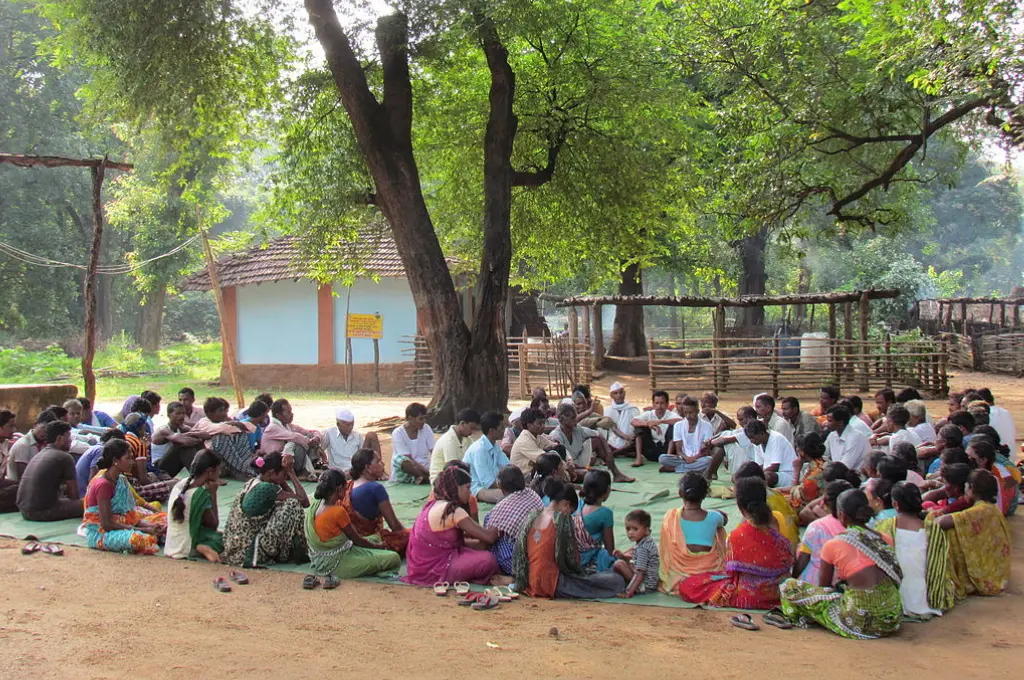
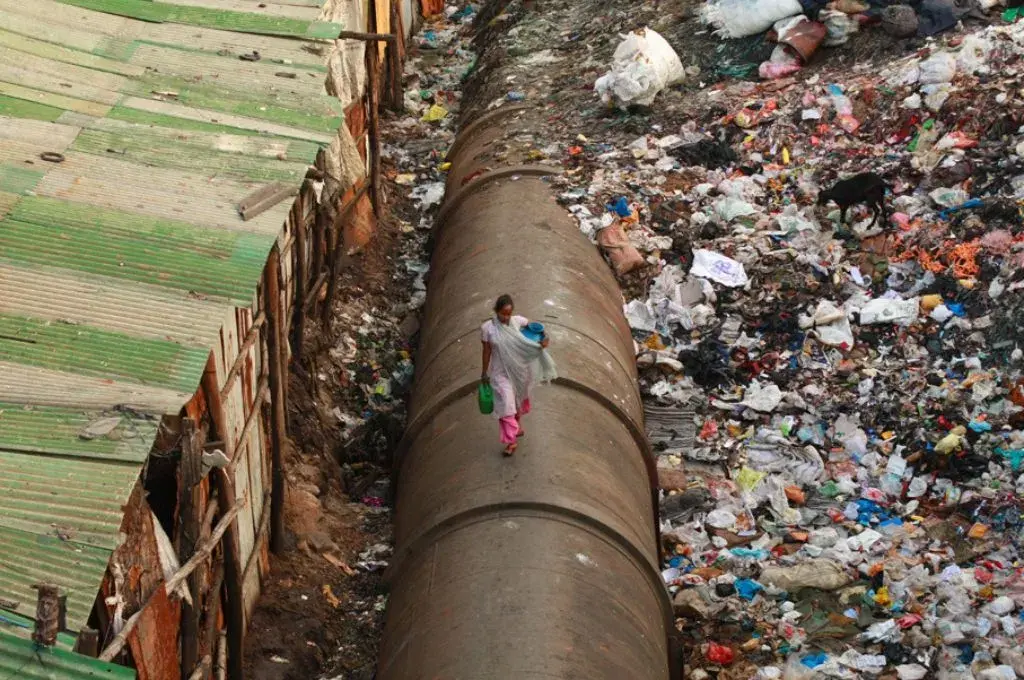
Some years ago, while speaking to a gram panchayat (GP) member in Karnataka, I mentioned that based on a rough calculation, the overall funds allocated to his GP under different government programmes and schemes was close to INR 8 crore per annum. He was surprised and remarked wryly, that with such funds, his GP—which represented a population of 8,500 people—could pave its roads with gold. This is the oft-repeated angst among panchayats: they either don’t have funds or don’t have visibility into the quantum of funds being spent in their areas by government departments. In most states, GPs—which are rural local governments—are mandated to plan and implement programmes to fulfil local priorities. However, they have visibility into a mere 10-15 percent of the funds spent in their area. While centrally- and state-sponsored schemes are implemented across villages in India, they are usually managed by line departments or specially created missions. As a result, the priorities are set externally. Is this likely to yield desired results?
The Right to Education Act has ensured the presence of schools every one and three kilometres, for primary and upper primary levels respectively, but teachers may not be present in schools; many vulnerable families are left out of social security programs; and common property resources, such as water bodies and pasture lands are abandoned. I believe that these and other last-mile issues exist, because they cannot be addressed from the distance of a state, a district, or even a block. They need to be addressed by a local institution. In other words, we need to follow the principle of subsidiarity—according to which a central authority should have a subsidiary function, performing only those tasks that cannot be performed at a local level—albeit with its checks and balances, if we hope to resolve local issues, sustainably and systemically.
Panchayats at the local level are mandated to plan and implement plans for economic development and social justice (Article 243G, Constitution of India). They can work on 29 functions including education, health, infrastructure, poverty alleviation, and agriculture. They are responsible for service delivery, as well as securing equal opportunities for their citizens, irrespective of caste, religion, wealth, gender, and race.
Panchayats, specifically GPs, are also the first institutions of democracy, closest to the people. They are elected bodies in which 30 lakh members (with 50 percent reservation for women in most states) are enrolled after contesting elections that typically have double or triple the number of aspirants. Imagine 100 lakh people thinking about and contemplating their role in public life. The numbers are large and the potential to nurture a culture of responsible political leadership is immense, as is the opportunity to instil people’s participation in governance, not as beneficiaries, but as citizens.
There are many gram panchayats that demonstrate what is possible and help us believe in the potential of these institutions.
There are many GPs that demonstrate what is possible and help us believe in the potential of these institutions. One such panchayat is Pindarkon GP, located in Hazaribagh district of Jharkhand, a state which is at the bottom of the national Devolution Index. Since the panchayat was elected and took charge in 2015, footfalls to this GP have increased manifold. As one of the first initiatives, Pindarkon’s Mukhiya, Kamakhya Singh ensured completion of the half-constructed GP building; to replace the older and prevalent practice of citizens visiting the Mukhiya’s home for GP-related work. This required special efforts, as the construction of GP Bhawan was complete as per block-level records. The panchayat has secured many other achievements, including those which spur the local economy. For example, while just 10.6 percent of the net sown area in Jharkhand is under irrigation, Pindarkon GP has brought irrigation systems to each of its seven villages. And while Pindarkon is not an absolute exception, it is a minority.
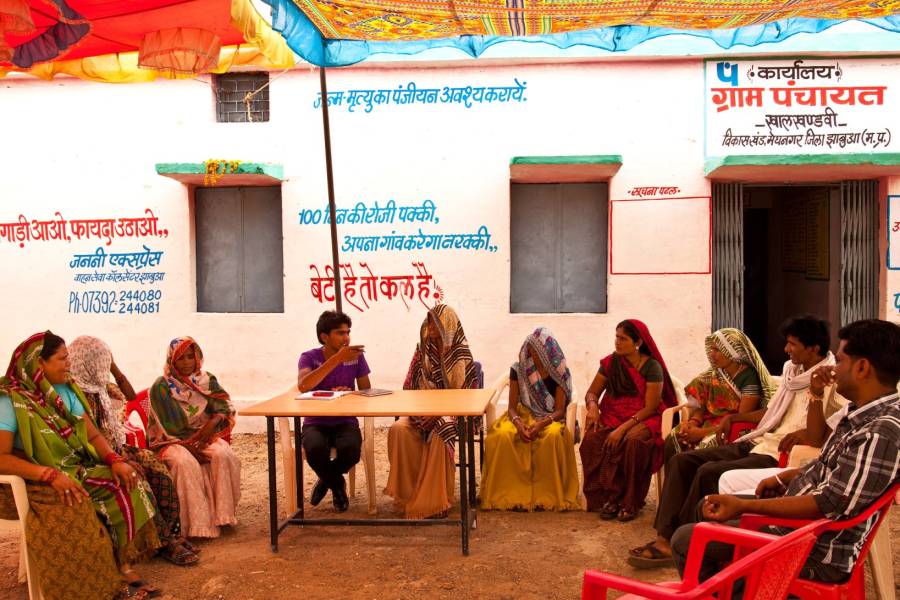

While functions are devolved to panchayats by most states, the devolution remains on paper. | Photo courtesy: UN Women/Gaganjit Singh on Flickr
Often panchayats are unable to rise above internal issues, lack systems and processes, and are dominated by a few powerful members. Moreover, the overall ecosystem does not enable these local governments to perform to their fullest potential. While functions are devolved to panchayats by most states, the devolution remains on paper. The lack of empowerment and lack of capacities become a vicious cycle. As a result of the lack of capacities in panchayats, government departments create parallel structures to deliver services, which in turn undermine panchayats’ autonomy and authority, leading to their disempowerment and weak capacities. And funding agencies, CSR, and civil society organisations often create their own service delivery mechanisms to efficiently implement programs at the village-level rather than get involved in the complex and time-consuming business of institution building.
We need to engage with and build capacities of local government institutions, rather than intervene directly.
We need to make a shift: to engage with and build capacities of local government institutions, rather than intervene directly. With the right support, panchayats can sustainably achieve results that others—state governments, funding agencies, and civil society organisations—will not be able to. This can also trigger change in the wider ecosystem to ensure government funds are allocated and spent on people’s priorities. While many issues are complex at the macro level, there are parts of these problems that are simpler to solve at the local level, if local institutions are equipped to handle them.
At Anode Governance Lab—an organisation that I founded to strengthen governance and enable public institutions to function more effectively—we recognise a few underlying principles to help panchayats perform as empowered local governments.
First, panchayats need to recognise and build on their constitutional identity and mandate as custodians of economic and social development of their area. A panchayat is a political organisation and a constitutional body. It is also a body corporate: it has a legal identity and is a legal entity. Despite this, panchayats are frequently treated like they are government departments, with state governments giving them targets and instructing them to implement programmes. Even well-intentioned nonprofits tend to treat panchayats like recipients.
While panchayats may collaborate with the state government and other bodies, they have the right to set their own priorities.
It is important for panchayats, and those working with them, to know that while panchayats may collaborate with the state government and other bodies, they have the right to set their own priorities.
Second, we need to respect and celebrate the primacy of elected members as upholders of grassroots democracy. Elected members of a panchayat are both custodians and users of local governance and services, making them the most suitable stakeholders to set development priorities. We need to help them understand and value their own strengths.
Third, we need to invest in institution building. An institution can only be effective if it is institutionally strong, and so we need to invest in building internal organisational capacity so that panchayats can manage and negotiate with various stakeholders, including other government agencies, to both prepare plans as well as to ensure their implementation. This requires strengthening and streamlining systems, structures, and processes.
Many provisions of organisation design can be leveraged from states’ Panchayati Raj Acts. For example, if we look at structures within a panchayat, the 29 functions and responsibilities are allocated to various Standing Committees. Strengthening these committees builds internal capability and distributes leadership. This entails articulating the role of a standing committee, building an understanding of the current situation, developing plans and strategies along with the members of these committees, and building the capacities required to execute these plans.
For those of us that work in rural areas in sectors such as agriculture, education, or health, we need to work with the elected representatives to understand and implement their local priorities. It may be a longer and more tedious path to start with, as it entails negotiating local politics and entrenched power structures. But in the long-term it proves to be more robust and sustainable.
Any intervention with panchayat institutions without an alignment with these principles violates the spirit of the 73rd amendment.
The potential to deepen grassroots democracy is immense if panchayats are accorded their place while visualising (and implementing) local development. At Anode, we have seen that it is possible to do this by bringing panchayats to the forefront.
—
Know more
- Read the 73rd and 74th constitutional amendments which institutionalised local self-government in India.
- Dip into data on gram sabhas and gram panchayats across the country.
- Learn about the current status of devolution and decentralisation of power in India.
Do more
- If you work with panchayats and want to explore ways in which your work can contribute to strengthening panchayat capacities, write in to info@anodegovernancelab.in.